Cancer tumor is always white, not green, blue or red
Surgical Pathology and Breast Cancers
Author: Colleen M. Powell, M.D., Assistant Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical CenterBREAST BIOPSY
Breast lesions suspected of being malignant are usually evaluated first by biopsy. Palpable (large enough to feel) masses can be directly excised. Sometimes, however, the lesion is detected only by mammography. In these cases the radiologist places a needle to guide the surgeon's excision. The needle, which remains in place, also identifies the radiographically abnormal area for the pathologist.
These excisions are performed in the operating room.
Diagnostic tissue can also be obtained using "needle biopsies" or "fine needle aspirations". These are less invasive procedures than excision and can be performed in the radiology department or the doctors office. "Needle biopsies" use a thin needle to obtain a small core of tissue which is sent to surgical pathology. An accurately performed needle biopsy produces tissue that is felt to be representative of the lesion. It is not an attempt to completely remove the mass or abnormality.
"Fine needle aspiration" (FNA) involves a similar procedure. With this method, cells from the suspicious area are aspirated and placed on a glass slides. This material is evaluated in cytopathology.
Both needle biopsies and fine needle aspirations are followed by an excisional biopsy if (1) cancer is present that needs to be removed or (2) the tissue core or aspirated cells are either non-diagnostic or suspicious for cancer and the clinician feels that further evaluation is indicated.
FROZEN SECTION EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS
Breast tissue is evaluated immediately in surgical pathology. First the pathologist describes the tissue and correlates what she sees with any accompanying radiographs. If the biopsy was performed for suspicious areas on mammography, it is determined that the lesion is present in the tissueremoved.

The pathologist then applies ink to the external surface of the specimen.
This is to identify the "surgical margin" or the plane cut by the surgeon.
The specimen is then sectioned to examine all areas.
When a grossly evident lesion is suspicious for malignancy, (see figure) a frozen section is performed. If cancer is found, and tissue is sufficient, a portion is then taken for special studies. (See "special studies")
After the frozen section the entire specimen is placed in formalin for fixation and preparation of glass slides for microscopic review and definitive diagnosis. Small biopsies are processed entirely. Larger specimens are generously sampled with special attention to visible lesions, fibrous or more firm areas and margins. All tissue adjacent to localizing needles is also evaluated microscopically.
DIAGNOSIS OF BREAST TUMORS
When the microscopic slides are examined for the final diagnosis, the pathologist pays special attention to certain details. These are: tumor size, type and grade, size of invasive component, lymphatic or vascular invasion, extent of the in-situ component, surgical margins, lymph nodes (when available) and background changes. Each of these issues will be discussed separately below.Type of tumor
The breast contains acini and ducts necessary for the production and secretion of milk. The acini are clustered together in lobules. The ducts and lobules are supported by stroma consisting of fibrous tissue and fat.Malignant cells may be confined to the ducts and acini (lobules). In these cases the tumor is called "in-situ" meaning that it has remained where it began and has not invaded the supporting stroma.
In-situ carcinomas are divided into (1) "ductal-carcinoma-in-situ" or "intraductal carcinoma" and (2) "lobular-carcinoma-in situ".
Intraductal carcinoma is considered a pre-invasive lesion; given time many would progess to invasive carcinoma. These lesions need to be completely excised. (see "Surgical margins" and "Extent of intraductal carcinoma").
Lobular-carcinoma-in situ is not considered pre-invasive but is felt to be a strong predictor of future new breast carcinoma in either the same or the opposite breast. For these reason, while it is important to document the presence of lobular-carcinoma-in-situ, it is not currently considered necessary for it to be completely excised.
Malignant cells that have moved out of the duct or acini (lobule) into the stroma are called "invasive" or "infiltrating" mammary carcinomas. Infiltrating (invasive) tumors are divided into
Malignant cells able to escape the duct or lobule are more aggressive and capable of spreading beyond the breast to adjacent lymph nodes and distant sites (ie metastasize).
"Breast cancer" can include any combination of in-situ and infiltrating carcinoma.
SIZE OF TUMOR
Tumor size, recorded at the time of frozen section examination, is included in the final pathologic diagnosis. Some tumors, too small to be appreciated in the whole specimen, are only seen microscopically. In these cases, the size of the tumor is measured from the glass slide.Although some tumors are composed entirely of infiltrating or invasive tumor cells, many are a combination of in-situ and infiltrating carcinoma. In these tumors the percentage of intraductal carcinoma is estimated. (See "Extent of intraductal carcinoma").
Tumors which are predominantly intraductal with only small areas of invasion are called "microinvasive". The microinvasive areas are described and measured on the glass slide if possible.
The size of the invasive component, as well as whole tumor size, is important to assess prognosis and direct therapy. Generally tumors with smaller areas of invasion do better.
TUMOR GRADE
The appearance of the malignant cells and the pattern of their invasion into the stroma varies between tumors. Tumors that most closely recapitulate the normal tissue are considered to be "low-grade" (well-differentiated). Tumors that bear little resemblance to the tissue they arose from are called "high-grade" (poorly differentiated) Some tumors represent an "intermediate grade" (moderately differentiated) between the other two extremes.Intraductal carcinoma is subclassified according to its pattern of growth into
- cribriform
- papillary
- micropapillary
- solid
- comedo
carcinoma
LYMPHATIC OR VASCULAR INVASION
The pathologist documents the presence or absence of tumor cells (tumor emboli) in lymphatic or vascular channels . The presence of "tumor emboli" signify increased risk of (1) subsequent distant metastases and (2) local recurrence in patients treated with breast conservation therapy.SURGICAL MARGINS
The surgical pathologist evaluates the resection margin identified by the black ink applied to the original specimen. The presence or absence of intraductal carcinoma or infiltrating tumor (ductal or lobular) at the margin is documented. Tumor at the surgical margin raises the concern that the primary tumor may not have been completely removed. Some tumors need to be re-excised to make sure the margins are free of tumor. Other tumors may be managed with appropriate adjustments of the scheduled radiation therapy.EXTENT OF INTRADUCTAL CARCINOMA
It has been shown that breast cancers with an extensive intraductal component are more likely to recur after conservative breast therapy. The pathologist documents the presence or absence of extensive intraductal malignancy. If the main tumor contains significant intraductal carcinoma and intraductal carcinoma is seen in the surrounding breast tissue, then "extensive intraductal carcinoma" is present.MULTIPLE FOCI OF CARCINOMA
Because it is important in prognosis and therapy planning, the pathologist also documents whether the malignancy is confined to one area or is seen in multiple foci.AXILLARY LYMPH NODE STATUS
Axillary lymph nodes are usually removed in patients with invasive breast carcinoma. The pathologist examines the lymph nodes for metastatic tumor. The total number of lymph nodes recovered and the number containing tumor are documented. Generally patients are stratified as (1) no tumor seen (2) 1-3 affected nodes (3) 4-9 affected nodes and (4) more than ten affected nodes. It is also noted whether tumor is present in the fibrous-fatty tissue around the lymph nodes or if multiple lymph nodes are matted together cancer. Treatment options are partly based on the number of involved lymph nodes (called "nodal status")BACKGROUND CHANGES
The benign changes in the breast are also described. "Fibrocystic changes" include the formation of cysts, increased fibrous tissue, benign patterns of duct or lobule distortion, and benign cellular changes.(Figure). The cells lining ducts or acini (lobules) may show increased growth without evidence of malignancy. This change is called "duct hyperplasia" (or "papillomatosis").
Sometimes the cells in duct hyperplasia are atypical (abnormal but not cancerous). Significant duct hyperplasia, especially if atypia is present, places the patient at an increased risk of subsequent breast carcinoma. Benign hyperplasia can also be seen in the acini (lobules) where it is called "lobular hyperplasia" or "atypical lobular hyperplasia" if some cellular abnormalities are seen. Atypical lobular hyperplasia, like lobular-carcinoma-in -situ, is not pre-invasive but is associated with an increased risk of subsequent breast malignancies.
Because they serve as a markers of increased risk of subsequent breast cancer, "duct hyperplasia", "atypical duct hyperplasia", "lobular hyperplasia", and "atypical lobular hyperplasia, are documented if present. However, like lobular-carcinoma-in-situ, these changes are not considered pre-invasive and no attempt is currently made to remove all tissue with these changes.
MASTECTOMY
When clinically indicated, the entire breast is removed. There are several types of mastectomy and all of these operations remove the entire breast.The pathologist evaluates mastectomies similar to biopsies. Ink is applied to the surgical margin and the tissue is serially sectioned and inspected. If there has been a previous biopsy, the surgical incision and biopsy cavity are described. Since the entire specimen cannot be examined microscopically, standard sections are submitted. If present, the biopsy cavity is generously sampled looking for residual tumor. Additional suspicious areas are also taken for microscopic evaluation. Finally, representative sections of each of the four breast quadrants, skin and nipple are submitted for review. If present, all lymph nodes are also evaluated. Because the entire specimen is not examined microscopically, it is possible that microscopic tumor foci have not been discovered. This is not currently considered to be a problem since the entire organ has been removed.
MICROCALCIFICATIONS
Small deposits of calcium can be seen on mammography. If their pattern is suspicious for cancer, a needle is placed to direct the surgeon and the pathologist. An xray of the specimen after surgery is usually performed and the radiograph sent to pathology with the biopsy. This allows the pathologist to confirm that the calcifications are present in the excised material. When examining the specimen microscopically, the pathologist notes the presence or absence of the calcifications. Although some calcifications seen on mammography cannot be seen by the pathologist, most are visible. Presence of calcifications in the microscopic sections re-assures the pathologist that she has examined the pertinent areas.CONTROVERSIES IN BREAST PATHOLOGY
The practice of pathology is part science and part art. While there is general diagnostic agreement among pathologists, some issues generate debate. Studies have shown that a panel of recognized expert breast pathologists can fail to reach consensus on certain controversial breast lesions.SPECIAL STUDIES
Both frozen and routine microscopic sections are traditionally stained with a combination of the dyes eosin and hematoxylin which color the cell nuclei blue and the cytoplasm pink. Additional staining methods, focused on specific cellular elements, are used when indicated. "Immunohistochemical" stains utilize specific antibodies to cellular constituents."Special" stains utilize chemical reactions to impart different colors to molecules of interest.
Traditionally the amount of tumor estrogen and progesterone hormone receptors has been determined using a biochemical test. This method requires fresh tissue obtained at the time of frozen section. Estrogen and progesterone hormone receptors can also be studied with immunohistochemical stains.
Immunohistochemistry can use either fresh tissue (cut onto slides at the time of frozen section) or tissue that has been processed and embedded in wax. This method is especially useful for small tumors that were either not large enough to be seen in the original (unprocessed) specimen or too small to spare tissue for special studies. The status of these hormone receptors is used to direct hormonal therapy.
Fresh tissue, if sufficient at the time of initial evaluation, is also obtained for "flow cytometry". Flow cytometry quantifies both the rate of tumor cell growth and the amount of nuclear DNA. This data can help determine prognosis and direct therapy.
Other immunohistochemical markers, performed in experimental protocols, are currently being studied in breast tissue. It is hoped that, in the future, some of these will prove useful in guiding therapy.http://www.carelife.com/cancer/surg_onc/Surgpath-breast.html
____
Cancer tumor is always white, not green, blue or red
Invasive Breast Carcinoma (IBC)
Images of invasive breast cancer:
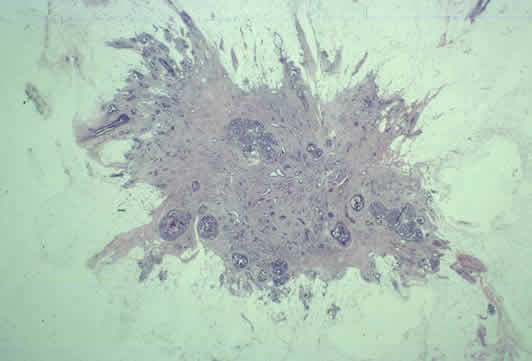
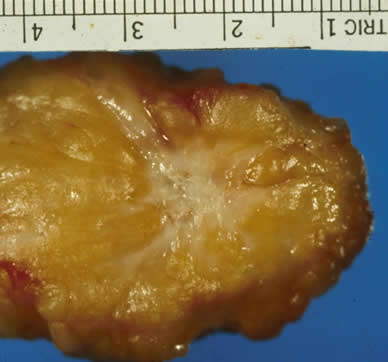


Left: Pathology slide image of cancerous breast tissue, Right: Tumor (white area) in fatty breast tissue.
Images courtesy: C. Whitaker Sewell, MD - Professor of Pathology, Emory University School of Medicine. https://www.cancerquest.org/patients/cancer-type/breast-cancer__
Images courtesy: C. Whitaker Sewell, MD - Professor of Pathology, Emory University School of Medicine. https://www.cancerquest.org/patients/cancer-type/breast-cancer__
Carcinoma of the breast is the most common cancer in the Western world and accounts for 20% of all cancers in women in the UK, with 1 in 10 women developing breast cancer in their lifetime (the prevalence of the condition in males is significantly less).
By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2019)
Invasive carcinoma of the breast can beclassified into:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (75-85%)
- Invasive lobular carcinoma (10%)
- Other subtypes (5%), such as medullary carcinoma or colloid carcinoma
- it is now known that almost all breast carcinomas actually arise in the terminal duct lobular unit but this classification remains in use due to the different behaviour of the two subtypes.
___________
Candida albicans fungus behaves exactly like a cancer tumor
(of genes Genome Inventory (as of November 27, 2014) , Metabolism, germ tubes and metastasis) of Candida albicans tumors
Estrogens is reported to have a significant impact on the spread of diverse and kaksimuotoisten fungi.
The effect of estrogen related to difference between the sexes, and the second dual mode, the pathogenic fungus, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis infection, which in contrast to the yeast Candida albicans infection step is pathogenic, i.e. cause disease state.
In healthy subjects, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis sticks mainly to adult men.
Diseases and problems caused by Systemic yeast infections are quite disparate, as well as life-threatening.
The reason for this are many different mushrooms that you can possibly get from food, the environment, and Candida infection. These fungi are able to release the more than 100 known to mycotoxins (mycotoxins).
Mycotoxins can affect various parts of the body and apparently unrelated ways. For example, one person can get adult acne, the next of arthritis and the other person's heart disease, fungi and mycotoxins can cause all of these diseases.
Systemic yeast infections are usually caused by Candida albicans or Candida tropicalis, intestinal hyperplasia position, although there are many other common fungi can cause or mimic the same symptoms and conditions for these diseases. They can also be caused by mold spores without such Asperigillus, which is very common in rural and urban communities. People may be exposed to in the workplace and at home the vastness of such quantities of airborne fungi (spores), which are the cause of many respiratory infections and allergies each year.
Understanding Candida, yeast and fungi structure
In order to obtain a successful treatment, are we to understand Candida, yeast and fungus structure. It really is your own way of life, appearing partly as a plant, animal and bacterial in nature. It is this ability to adapt and change shape, or its deformation, which causes it to be so difficult to eradicate from the human body. Once we understand its composition, we can successfully treat it with natural methods without damaging the body, so that it does not have immunity.
Candida albicans visualised using scanning electron microscopy
Mushrooms belong to the group of organisms called eukaryotes, have complex with the cell structures and in which cells have a nucleus, a nucleus or nucleating.
Animals and plants allocation among the various cell types of the nucleus, bacteria are not.
Fungal cell wall is composed of mannoproteins and chitin, which themselves consist of cellulose and starch. Chitin is a vegetable nature and gives the cell its rigidity , (cf. Insects and crayfish).
The cell wall is close to the same composition as vegetables, which makes them get up and grow by reaching toward the sunlight. It consists of a one-cell-thick filaments, strands, often referred to as mycelium , being very similar to the roots of the plants, because they feed on fungi (glucose) of the mycelium.
These roots, mycelia, can quite easily pierce the human intestinal walls and tissues of the human body and to create, for example. Leaky gut syndrome and other negative effects.
- SEE VIDEO -
Within the cell is a membrane, the membrane consisting of proteins and fats, also known as lipoprotein, which is common, similar to the cell structure in animals and humans.
In the center is the core, and together with the nucleating film over the lipoprotein is a "vegetable" cell wall, which has allowed the classification of fungi belonging to the animal kingdom, although they multiply asexually, in many cases, by producing spores germ tubes (see Fig. Germination).
They can also copulate with other fungal mycelium when the two meet, which can generate two multinucleus ball-shaped cells that join together to form the new kernel. Asexual distribution is very similar to the bacteria, which are simply divided, and each cell contains the same even if the chromosomes of the bacteria has no core.
Fungal spores are, therefore, the ability to divide.
_
http://portti.iltalehti.fi/keskustelu/showthread.php?t=1002780&page=2
Candida understanding, yeast and fungi structure
In order to obtain a successful treatment, are we to understand Candida, yeast and fungus structure. It really is your own way of life, appearing partly as a plant, animal and bacterial in nature.
It is this ability to adapt and change shape, or its deformation, which causes it to be so difficult to eradicate from the human body.
Once we understand its composition, we can successfully treat it with natural methods without damaging the body, so that it does not have immunity.
Fungal structure
Mushrooms belong to the group of organisms called eukaryotes, have complex with the cell structures and in which cells have a nucleus, a nucleus or nucleating.
Animals and plants allocation among the various cell types of the nucleus, bacteria are not.
Fungal cell wall composed of chitin and mannoproteins, which themselves consist of cellulose and starch.
Chitin is a vegetable nature and gives the cell its stiffness (f. ex... Insects and crayfish).
The cell wall is close to the same compositions as vegetables, which makes them get up and grow by reaching toward the sunlight. It consists of one cell thick filaments, strands, often referred to as the mycelium is therefore very similar to the roots of the plants, fungi because they feed (glucose, a grape sugar) of the mycelia.
In order to obtain a successful treatment, are we to understand Candida, yeast and fungus structure. It really is your own way of life, appearing partly as a plant, animal and bacterial in nature.
It is this ability to adapt and change shape, or its deformation, which causes it to be so difficult to eradicate from the human body.
Once we understand its composition, we can successfully treat it with natural methods without damaging the body, so that it does not have immunity.
Fungal structure
Mushrooms belong to the group of organisms called eukaryotes, have complex with the cell structures and in which cells have a nucleus, a nucleus or nucleating.
Animals and plants allocation among the various cell types of the nucleus, bacteria are not.
Fungal cell wall composed of chitin and mannoproteins, which themselves consist of cellulose and starch.
Chitin is a vegetable nature and gives the cell its stiffness (f. ex... Insects and crayfish).
The cell wall is close to the same compositions as vegetables, which makes them get up and grow by reaching toward the sunlight. It consists of one cell thick filaments, strands, often referred to as the mycelium is therefore very similar to the roots of the plants, fungi because they feed (glucose, a grape sugar) of the mycelia.
These roots, mycelia, can quite easily pierce the human intestinal walls and tissues of the human body and to create, for example. Leaky gut syndrome and other negative effects.
Within the cell is a membrane, the membrane consisting of proteins and fats, also known as lipoprotein, which is common, similar to the cell structure in animals and humans.
In the center is the core, and together with the nucleating film over the lipoprotein is a "vegetable" cell wall, which has allowed the classification of fungi belonging to the animal kingdom, although they multiply asexually, in many cases, producing spores, germ tubes (see Fig. Germination).
They can also copulate with other fungal mycelia between the two, which may generate two multinucleus spherical cells, which are joined together to form a new core.
Asexual distribution is very similar to the bacteria, which are simply divided, and each cell contains the same even if the chromosomes of the bacteria has no core.
Fungal spores are, therefore, the ability to divide.
Candida albicans tumor
Tumors are Perceived as one phenomenon. Tumors are one phenomenon, but there are many types. Why?
According to official views see that genetic alteration at the basis of neoplastic development, it is possible that the alteration can manifest itself in any environment with all possible typological differentiations.
According to official views see that genetic alteration at the basis of neoplastic development, it is possible that the alteration can manifest itself in any environment with all possible typological differentiations.
These behaviors are a function of the quantity and quality of the affected tissues. An organ whose connective tissue has been Invaded defends itself with cellular hyper-productions That attempt to encyst the fungin colonies Which are trying to completely colonize the organism .
http://www.curenaturalicancro.com/en/candida-albicans-microbiological/
http://www.curenaturalicancro.com/en/candida-albicans-microbiological/
___
Do You Have Candida? Take The "Spit Test"!
___
Candida Genome Database
The Candida Labs Page is a list of laboratories working on Candida around the world.Candida colleagues are invited to enter information into Their colleague CGD using the Colleague Submission / Update Form. The page displays contact information, links to web pages, gene names and keywords as provided by Candida colleagues.
Please use the Colleague Submission / Update Form to update your colleague information in CGD. Display all Candida Labs
_
Http://fi.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kitiini _
hypha
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypha
_
Somatic hyphae
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatic_hyphae
_
1- hyphal septum wall 2- 3- 4- Mitochondrion vacuole 5- Ergosterol Crystal Nucleus 6- to ribosomes 7- 8- 9- endoplasmic reticulum Lipid body 10 to the plasma membrane Spitzenkörper 11- 12- Golgi apparatus
http: // en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HYPHAE.png
_
Germ tubes
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Germ_tubes
_
Germination
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Germination
_
mycelium - mycelium - is the vegetative part of a fungus
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycelium
_
opportunistic mycelial Fungal Infections in Organ Transplant Recipients
http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/37/2/221.full.pdf
_
Fungal hyphae Cells
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypha
_____
Candida Symptoms

Candida is such a difficult condition to diagnose because it can affect each sufferer in a different way, on a different part of their body, in a way that may even be unique to that person.
For this reason, Candida is often misdiagnosed and the symptom is treated instead of the underlying cause, rather like taking a lozenge for a throat infection!
Practically, patients often have to diagnose themselves because the symptoms of Candida are so confusing.
![]()
The consensus is that many more ![]() people are suffering from Candida than those few who are diagnosed correctly. You may find yourself suffering from any or all of the following symptoms if you have Candida:
people are suffering from Candida than those few who are diagnosed correctly. You may find yourself suffering from any or all of the following symptoms if you have Candida:
The Way You Feel
Inability to focus, Poor memory, Brain fog, Irritability, Anger, Dizziness, Depression, Crying spells, Panic attacks
, Low libido, Persistent extreme fatigue, Hyperactivity, Cravings for sweets and alcohol, Insomnia, Poor coordination.
Your Digestive System
, Bloating, Flatulence, Nausea, Diarrhea, Constipation, Stomach cramps, Indigestion, Burping after meals, Mucus in stool, Hemorrhoids, Itching anus.
Your Skin
Acne, Cysts, Hives, Night sweats, Psoriasis, Eczema, Dermatitis, Fungal infections of the nails & skin, Athlete’s foot, Body odor
Your Mouth
Thrush (white coating on tongue), Swollen lower lip, Halitosis, Metallic taste in mouth, Bad breath, Canker sores
, Bleeding gums, Cracked tongue.
Your Respiratory System
Persistent cough, Mucus in throat, Sore throat, Sinus congestion
, Chronic post-nasal drip, Flu-like symptoms, Hay fever symptoms, Sinusitis, Asthma.
Your Ears And Eyes
Eye pain, Itchy eyes, Sensitivity to light, Blurred vision, Bags under eyes, Ringing in the ears, Ear infections.
Your Genito-Urinary System
Recurring yeast infections
, Recurring UTI’s (urinary tract infections), Cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), PMS & menstrual irregularities, Fungal rash.
Your Immune System
Frequent colds and flu, Allergies, Sensitivities to food, fragrances and chemicals.
Your Weight
Other Symptoms
Check out our Candida Questionnaire to see if you might have excess Candida growth.
Expert Leon Chaitow says in his book that, “Candida is possibly the least understood, most widespread cause of continuing ill health currently in our midst.” Think of all the people suffering from the above symptoms, think of the number of times that you yourself have suffered from them, and you can see how this might be true!
Expert Leon Chaitow says in his book that, “Candida is possibly the least understood, most widespread cause of continuing ill health currently in our midst.” Think of all the people suffering from the above symptoms, think of the number of times that you yourself have suffered from them, and you can see how this might be true!
Candida Misdiagnosis
Your doctor might confuse any of the following conditions with Candida. The reason is that the symptoms are often exactly the same, and Candida may manifest itself in any combination of those symptoms.
We have listed here some of the possible misdiagnoses, together with the symptom that your doctor has focused on. Remember, your doctor is relying on you for an accurate description of your symptoms, so make sure you tell him everything!
, bloating, gas, diarrhea, indigestion
Arthritis - joint pain
- constant fatigue
Diaper Rash - rashes and itching in infants
Athlete’s Foot - Fungus on toenails
Crohn’s Disease - abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, indigestion
Gastroenteritis - abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, indigestion
A Candida misdiagnosis may actually worsen your Candida overgrowth. If your doctor believes that you have IBS, Crohn’s Disease or Gastroenteritis, he may prescribe the anti-inflammatory Cortisone. This introduces steroids to the gut, which can increase the growth of Candida colonies.
Foods to Control Candida
If you struggle with Candidiasis, dysbiosis or cancer, it may be to your benefit to dig deeper into the candida theory and Dr. Simoncini’s website which advocates sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) treatments. Baking soda is alkalizing and it neutralizes tumors.
In order to avoid an acidic inner body environment, dedicate yourself to a life of eating an alkaline diet. Dr. Douglas Graham explains here how to safely & smartly eat an alkaline diet which can keep candida balanced in the body.
- http://www.mineral-well.com/eng_remedy11.html
- http://fashionviral.net/healthcare-diet-to-lose-weight-the-acid-alkaline-balance-human-blood-ph-should-be-slightly-alkaline-7-35-7/
- https://www.mindbodygreen.com/0-5165/Alkaline-Acidic-Foods-Chart-The-pH-Spectrum.html
- http://blog.envole.net/alkaline-food-for-energy/
- https://trans4mind.com/nutrition/pH.html
- http://www.alkalinesisters.com/alkaline-food-chart/
- http://thesweetvegan.com/alkaline-rich-foods-vs-acidic-food-chart/
- http://smp1993.it/acidosi-regolazione-del-ph/
- https://www.collective-evolution.com/2015/09/10/signs-your-body-is-too-acidic-how-to-correct-it/
- https://www.collective-evolution.com/2015/09/10/signs-your-body-is-too-acidic-how-to-correct-it/
- http://phwater.com.ua/2017/11/26/produkty-okislyayushhie-ili-oshhelachivayushhie-organizm/
___
Is Cancer Caused By Candida?
Anywhere between 79 to 97% of all cancer patients also have Candidiasis
Balance…it’s so important: work-home, acid-alkaline, yin-yang, light-dark, activity-rest, public-private, belief-skepticism and so forth. Life feels harmonious, bodies feel strong, and minds & hearts feel clear when we’re in balance.
 One of the many elements to good health is maintaining a balance of Candida albicans, an intestinal fungus in the medley of gut flora. Candida lives in 80% of the human population without causing harmful effects, although overgrowth of the fungus results in a condition called Candidiasis.
One of the many elements to good health is maintaining a balance of Candida albicans, an intestinal fungus in the medley of gut flora. Candida lives in 80% of the human population without causing harmful effects, although overgrowth of the fungus results in a condition called Candidiasis.
In the plant world, carcinoma is caused by fungal infections, and the same happens in humans. Fungi always carry a tumor with them – this has been proven in both in vivo and in vitro studies.
However, scientists believe that they develop after the disease appeared. Dr. Simonchini believes that they were already there before – fungi create cancer, weaken our immune system and then attack the whole body.
Candida:
Cancer is Fungus 1 of 2
Every type of cancer is caused by the Candida fungus, which has been confirmed by several studies, and its histological structure is a result of the defensive measures against the invasion. Over time, our tissues are weakened and tired, and they start producing unidentified cells.
According to Dr. Simonchini, cancer is an “ulcer” where deformed cells accumulate and form colonies. Baking Soda: The usual antifungal drugs are ineffective against cancer as they only attack the surface of the cells. The main infection is more powerful than a single bacterium, which is why fungal infections last for so long. “I have identified the things that can attack these colonies of fungi – for cancer, it's baking soda, and a iodine tincture is the best substance for skin cancer,” claims Dr. Simonchini.
Many studies have confirmed baking soda's intracellular action against cancer.
The Treatment:
“I have used the treatment on my patients for more than 20 years.
Many of these patients have completely recovered from the disease, even when doctors gave them no chances. The best way to eliminate a tumor is for it to come in contact with baking soda, which can be applied as an enema for digestive cancers, intravenous injection for brain and lung tumors and inhalation for tumors in the upper respiratory system.
Breast, lymph system and subcutaneous tumors can be treated with a local perfusion.
Internal organ tumors should be treated with baking soda by applying it directly into the arteries, and it's also important to treat every type of cancer with the proper dose,” Dr. Simonchini explains, and continues: “For phleboclisis, you'll need about 500 cm. of 5% or 8.4% solution; in some cases, the mixture only needs to be salty enough.
During every treatment, it's important to know that tumor colonies come back between the 3 and 4 day, and suffer a collapse between the 4 and 5 day, so a minimum of 6 days of treatment is required. The treatment should be repeated for 4 cycles, and has no other side-effects other than thirst and weakness.”
“For skin cancer, you should rub a 0.7% iodine tincture on the affected areas 20-30 times a day.
Afterwards, the tumor will not return,” Dr. Simonchini says.
Here are the main symptoms of Candida infection:
Chronic fatigue; Obsessive-compulsive disorder; Anxiety and irritability; Brain fog and nausea; Chronic skin disorders; Chronic digestive disorders; Mood changes; Starch and sugar cravings. If you have notice at least 2 of these symptoms, you may have an advanced stage of candida infections which may result in cancer, so they should never be ignored.
Treatment And Prevention Of Candida Infections:
The fungal development must be kept in check. Left untreated, candida can lead to candidiasis which can cause symptoms that mimic other diseases and result in perforation in the intestines and leaky gut syndrome. This will allow protein to attack your blood cells. In order to prevent further problems, we first need to eliminate the foods that feed candida – sugar and starch.
This means no bread, candy, fresh fruit, pasta and rice for a while. Focus on eating raw fruit and steamed vegetables, and some people have had great results with grapefruit seeds. Dr. Simonchini recommends using aluminum-free baking soda for the treatment of cancer. It can be found in almost all health stores and pharmacies.How The Therapy Works:
Baking soda significantly increases the alkalinity of your blood which destroys the fungi. Due to this, baking soda quickly disintegrates the tumor, leaving it without defense.
Dr Tullio Simoncini explaining the simple cure for cancer
For stomach, colon, rectal and oral cancer, you need to take 1 teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water every morning and evening for a month. In most cases, this is enough time to eliminate the tumor.
The therapy should last 3-4 weeks and not a day more. Dr. Simonchini's therapy also usually requires intravenous injections as well. For best results, you'll need 500 ml. of 5% baking soda solution applied in the vein directly every day.
Do this for 24 days, then go for a scan.
Vaginal fungal infections have become pretty common nowadays and according to Dr. Simonchini, they are the main culprit for cervical cancer and vaginal tumors. In order to treat these problems, you need to wash your vagina with a mixture made of 2 l. of filtered water and 2 tablespoons of baking soda. This will defeat the fungi that are causing the problem and prevent them from coming back in the future. Related: Astonishing Evidence: Coconut Oil And Baking Soda Can Kill Cancer Baking Soda – True Enemy Of The Pharmaceutical Industry Video: Any Type Of Cancer Can Be Cured In Just 2-6 Weeks
Read more at:
http://www.social-consciousness.com/2017/03/doctor-who-shocked-world-cancer-fungus-can-be-treated-with-baking-soda.html
Related: Astonishing Evidence:
- Coconut Oil And Baking Soda Can Kill Cancer
- Baking Soda – True Enemy Of The Pharmaceutical Industry
- Video: Any Type Of Cancer Can Be Cured In Just 2-6 Weeks
Dr. Simoncini, an Italian oncologist, claims that the root cause of cancer is Candidiasis.
• …anywhere between 79 to 97 percent of all cancer patients also have Candidiasis. Dr. Simoncini’s research has led him to believe that something as simple as a fungus, Candida albicans, is the leading cause of cancer; that cancer itself is in fact a fungus. What we refer to as a tumor is nothing more than a body’s attempt at protecting itself from that fungus by encapsulating it.
• A good sign that Candida is out of balance in the body is feeling “run down” and developing a craving for sugars and carbohydrates, as this is the main fuel for the growing amounts of yeast in the intestine. The more sugar and grains eaten, the more the yeast grows out of control. Eventually, this will weaken the immune system, which, in turn, can allow it to infiltrate various other organs.
If you are interested and have 26 minutes to invest, watch this fascinating video from Dr. Simoncini’s website:
Dr. T. Simoncini - Cancer Is A Fungus And Is Completely Curable
The imbalance in intestinal flora, sometimes called dysbiosis, can also lead to other more common, and less lethal, health problems such as:
- Vaginitis
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Weight gain
- Food allergies
- Migraines
- Asthma
- Depression
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Thrush
Excerpts from the Essential Oils Desk Reference:
• Fungal cultures such as candida excrete large amounts of poisons called mycotoxins as part of their life cycles. These poisons must be detoxified by the liver and immune system. Eventually they can wreak enormous damage on the tissues and organs and are believed to be an aggravating factor in many degenerative diseases such as cancer, arteriosclerosis, and diabetes.
Symptoms of Systemic Fungal Infection:
- Fatigue/low energy
- Overweight
- Low resistance to illness
- Allergies
- Unbalanced blood sugar
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Indigestion
- Colitis and ulcers
- Diarrhea/constipation
- Urinary tract infections
- Rectal or vaginal itch
• Pathogenic microorganisms have a tendency to hibernate along the spinal cord and in the lymphatic system. The body has the ability to hold them in a suspended state for long periods of time. When the immune system becomes compromised from stress, fatigue or other factors, they can be released and manifest illness and disease. Essential oils of oregano, thyme, or hyssop along the spine using Raindrop Technique may help to drive the dormant fungi out of the spinal fluid.
____________
More about Candida:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
___
Treat candida and inflammations yourself
Balance…it’s so important: work-home, acid-alkaline, yin-yang, light-dark, activity-rest, public-private, belief-skepticism and so forth. Life feels harmonious, bodies feel strong, and minds & hearts feel clear when we’re in balance.
 One of the many elements to good health is maintaining a balance of Candida albicans, an intestinal fungus in the medley of gut flora. Candida lives in 80% of the human population without causing harmful effects, although overgrowth of the fungus results in a condition called Candidiasis.
One of the many elements to good health is maintaining a balance of Candida albicans, an intestinal fungus in the medley of gut flora. Candida lives in 80% of the human population without causing harmful effects, although overgrowth of the fungus results in a condition called Candidiasis.In the plant world, carcinoma is caused by fungal infections, and the same happens in humans. Fungi always carry a tumor with them – this has been proven in both in vivo and in vitro studies.
However, scientists believe that they develop after the disease appeared. Dr. Simonchini believes that they were already there before – fungi create cancer, weaken our immune system and then attack the whole body.
Candida:
Cancer is Fungus 1 of 2
According to Dr. Simonchini, cancer is an “ulcer” where deformed cells accumulate and form colonies. Baking Soda: The usual antifungal drugs are ineffective against cancer as they only attack the surface of the cells. The main infection is more powerful than a single bacterium, which is why fungal infections last for so long. “I have identified the things that can attack these colonies of fungi – for cancer, it's baking soda, and a iodine tincture is the best substance for skin cancer,” claims Dr. Simonchini.
Many studies have confirmed baking soda's intracellular action against cancer.
The Treatment:
“I have used the treatment on my patients for more than 20 years.
Many of these patients have completely recovered from the disease, even when doctors gave them no chances. The best way to eliminate a tumor is for it to come in contact with baking soda, which can be applied as an enema for digestive cancers, intravenous injection for brain and lung tumors and inhalation for tumors in the upper respiratory system.
Breast, lymph system and subcutaneous tumors can be treated with a local perfusion.
Internal organ tumors should be treated with baking soda by applying it directly into the arteries, and it's also important to treat every type of cancer with the proper dose,” Dr. Simonchini explains, and continues: “For phleboclisis, you'll need about 500 cm. of 5% or 8.4% solution; in some cases, the mixture only needs to be salty enough.
During every treatment, it's important to know that tumor colonies come back between the 3 and 4 day, and suffer a collapse between the 4 and 5 day, so a minimum of 6 days of treatment is required. The treatment should be repeated for 4 cycles, and has no other side-effects other than thirst and weakness.”
“For skin cancer, you should rub a 0.7% iodine tincture on the affected areas 20-30 times a day.
Afterwards, the tumor will not return,” Dr. Simonchini says.
Here are the main symptoms of Candida infection:
Chronic fatigue; Obsessive-compulsive disorder; Anxiety and irritability; Brain fog and nausea; Chronic skin disorders; Chronic digestive disorders; Mood changes; Starch and sugar cravings. If you have notice at least 2 of these symptoms, you may have an advanced stage of candida infections which may result in cancer, so they should never be ignored.
Treatment And Prevention Of Candida Infections:
The fungal development must be kept in check. Left untreated, candida can lead to candidiasis which can cause symptoms that mimic other diseases and result in perforation in the intestines and leaky gut syndrome. This will allow protein to attack your blood cells. In order to prevent further problems, we first need to eliminate the foods that feed candida – sugar and starch.
This means no bread, candy, fresh fruit, pasta and rice for a while. Focus on eating raw fruit and steamed vegetables, and some people have had great results with grapefruit seeds. Dr. Simonchini recommends using aluminum-free baking soda for the treatment of cancer. It can be found in almost all health stores and pharmacies.How The Therapy Works:
Baking soda significantly increases the alkalinity of your blood which destroys the fungi. Due to this, baking soda quickly disintegrates the tumor, leaving it without defense.
Dr Tullio Simoncini explaining the simple cure for cancer
For stomach, colon, rectal and oral cancer, you need to take 1 teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water every morning and evening for a month. In most cases, this is enough time to eliminate the tumor.
The therapy should last 3-4 weeks and not a day more. Dr. Simonchini's therapy also usually requires intravenous injections as well. For best results, you'll need 500 ml. of 5% baking soda solution applied in the vein directly every day.
Do this for 24 days, then go for a scan.
Vaginal fungal infections have become pretty common nowadays and according to Dr. Simonchini, they are the main culprit for cervical cancer and vaginal tumors. In order to treat these problems, you need to wash your vagina with a mixture made of 2 l. of filtered water and 2 tablespoons of baking soda. This will defeat the fungi that are causing the problem and prevent them from coming back in the future. Related: Astonishing Evidence: Coconut Oil And Baking Soda Can Kill Cancer Baking Soda – True Enemy Of The Pharmaceutical Industry Video: Any Type Of Cancer Can Be Cured In Just 2-6 Weeks
The therapy should last 3-4 weeks and not a day more. Dr. Simonchini's therapy also usually requires intravenous injections as well. For best results, you'll need 500 ml. of 5% baking soda solution applied in the vein directly every day.
Do this for 24 days, then go for a scan.
Vaginal fungal infections have become pretty common nowadays and according to Dr. Simonchini, they are the main culprit for cervical cancer and vaginal tumors. In order to treat these problems, you need to wash your vagina with a mixture made of 2 l. of filtered water and 2 tablespoons of baking soda. This will defeat the fungi that are causing the problem and prevent them from coming back in the future. Related: Astonishing Evidence: Coconut Oil And Baking Soda Can Kill Cancer Baking Soda – True Enemy Of The Pharmaceutical Industry Video: Any Type Of Cancer Can Be Cured In Just 2-6 Weeks
Read more at:
http://www.social-consciousness.com/2017/03/doctor-who-shocked-world-cancer-fungus-can-be-treated-with-baking-soda.html
Related: Astonishing Evidence:
Dr. Simoncini, an Italian oncologist, claims that the root cause of cancer is Candidiasis.
http://www.social-consciousness.com/2017/03/doctor-who-shocked-world-cancer-fungus-can-be-treated-with-baking-soda.html
Related: Astonishing Evidence:
- Coconut Oil And Baking Soda Can Kill Cancer
- Baking Soda – True Enemy Of The Pharmaceutical Industry
- Video: Any Type Of Cancer Can Be Cured In Just 2-6 Weeks
Dr. Simoncini, an Italian oncologist, claims that the root cause of cancer is Candidiasis.
• …anywhere between 79 to 97 percent of all cancer patients also have Candidiasis. Dr. Simoncini’s research has led him to believe that something as simple as a fungus, Candida albicans, is the leading cause of cancer; that cancer itself is in fact a fungus. What we refer to as a tumor is nothing more than a body’s attempt at protecting itself from that fungus by encapsulating it.
• A good sign that Candida is out of balance in the body is feeling “run down” and developing a craving for sugars and carbohydrates, as this is the main fuel for the growing amounts of yeast in the intestine. The more sugar and grains eaten, the more the yeast grows out of control. Eventually, this will weaken the immune system, which, in turn, can allow it to infiltrate various other organs.
If you are interested and have 26 minutes to invest, watch this fascinating video from Dr. Simoncini’s website:
Dr. T. Simoncini - Cancer Is A Fungus And Is Completely Curable
The imbalance in intestinal flora, sometimes called dysbiosis, can also lead to other more common, and less lethal, health problems such as:
- Vaginitis
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Weight gain
- Food allergies
- Migraines
- Asthma
- Depression
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Thrush
Excerpts from the Essential Oils Desk Reference:
• Fungal cultures such as candida excrete large amounts of poisons called mycotoxins as part of their life cycles. These poisons must be detoxified by the liver and immune system. Eventually they can wreak enormous damage on the tissues and organs and are believed to be an aggravating factor in many degenerative diseases such as cancer, arteriosclerosis, and diabetes.
Symptoms of Systemic Fungal Infection:
- Fatigue/low energy
- Overweight
- Low resistance to illness
- Allergies
- Unbalanced blood sugar
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Indigestion
- Colitis and ulcers
- Diarrhea/constipation
- Urinary tract infections
- Rectal or vaginal itch
• Pathogenic microorganisms have a tendency to hibernate along the spinal cord and in the lymphatic system. The body has the ability to hold them in a suspended state for long periods of time. When the immune system becomes compromised from stress, fatigue or other factors, they can be released and manifest illness and disease. Essential oils of oregano, thyme, or hyssop along the spine using Raindrop Technique may help to drive the dormant fungi out of the spinal fluid.
____________
__
eof















Ei kommentteja:
Lähetä kommentti